[NGW Magazine] Mitsubishi aims to expand LNG footprint
This article is featured in NGW Magazine Volume 2, Issue 17
By Audrey Raj
Japan’s Mitsubishi Corporation (MC) has been expanding its liquefied natural gas (LNG) presence rapidly in the last few years by investing in mega projects internationally and is now looking to tap into emerging markets going forward, while capitalising on the company’s Canadian and US investment.
Through its wholly-owned subsidiaries and joint venture companies, the Tokyo-headquartered trading company has been steadily increasing the value chain of its natural gas business on a global scale in North America, southeast Asia and Australia.
Over the years, it has emerged as a key LNG supplier to several Japanese utility and gas companies like Tohuku Electric, Tokyo Gas, Osaka Gas, Shanghai LNG, JX Nippon, Kansai Electric, Kyushu Electric, and Tohoku Electric.
Ryosuke Tsugaru, CEO at Diamond Gas International (DGI), an MC subsidiary specialising in the marketing, trading and shipping of LNG says MC believes that to some extent it has contributed to the LNG industry by opening up the market in north Asia, which is now being referred to as the traditional LNG market “In Japan and Korea, MC holds strong presence which remains the company’s core market. While being committed to serving the customers in these markets, MC is also trying to extend its reach as LNG demand grows worldwide,” he told NGW.
DGI is the latest in a series of energy subsidiaries set up by MC. DGI joint MC’s Singapore office in 2013, to oversee three major business areas: marketing of LNG produced by projects in the US and Canada in which MC has equity stakes; new business development in emerging LNG markets; and short-term LNG trading and optimisation.
US, Canada investment
In the US, MC is a shareholder of the $10bn Cameron LNG project, jointly owned by Sempra Energy (50.2%), French Engie (16.6%), Mitsui (16.6%), and Japan LNG investment (16.6%), a 70:30 company owned by MC and Nippon Yusen Kabashiki Kaisha (NYK).
Located in Louisiana, construction on the Cameron LNG regasification terminal started in August 2005 and commercial operations began in July 2009. It has two berths capable of accommodating Q-Flex LNG ships, three LNG storage tanks of 480,000 cubic meters, and regasification capacity of 1.5bn ft³/day.
In 2014, Cameron LNG began turning it around into export mode, building liquefaction facilities, comprising three trains capable of exporting up to 12mn metric tons/yr. Train 1 was originally slated to come online in early 2018, but Sempra said in August that this could be delayed into 2019, with the other two trains following throughout 2019.
Last year, Cameron LNG received approval from the US Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to expand the three-train liquefaction project to add two more trains, and a fifth LNG storage tank. The expansion project will be next to the LNG terminal and liquefaction facilities.
According to Tsugaru, MC is entitled to 4mn mt/yr of liquefaction capacity from Cameron LNG, and DGI has secured sales with multinational leading companies as its LNG buyers. He said although there are multiple new projects proposed in the US, Cameron LNG, being a brownfield project, stands well ahead of other proposed LNG projects in the country.
Commenting on how US supply projects in general are set to fare given the current over-supply in the market, he said: “In general, US LNG projects can be highly strategic developments. First, from the viewpoint of an LNG supplier, a project can be a swing LNG supplier to the Atlantic and Pacific markets by capitalising on an abundant natural gas supply in north America which brings optionality for plant expansion as well.
“Second, from the viewpoint of an LNG buyer, US LNG, if the transaction is based on the north American gas price, it brings a different set of price indices, contributing to the diversification of price exposures,” he added.
MC also holds natural gas assets in Canada which it is developing with its partner Encana. The firm is keen to find an optimum way to capitalise on the Canadian market through the development of an LNG project on the western coast of the country.
In 2014, MC together with Shell, PetroChina, and Kogas, inked an agreement to develop an LNG export project, LNG Canada, which has received the necessary regulatory approvals for development. To be built in Kitimat, LNG Canada will initially consist of two LNG trains each with the capacity to produce 6.5mn mt/yr and with an option to expand the project in the future to four trains.
Last year, the joint venture announced its decision to delay the final investment decision (FID) on LNG Canada that was planned for end 2016, citing global industry challenges, including capital constraints. This could change, however, as the companies are now targeting to take an FID within 2018.
“The LNG business remains one of MC’s main pillars in its business strategy going forward. We have 50 years of experience in the LNG industry and its typical role has been a strategic minority investor,” Tsugaru noted. “However, MC nowadays has expanded its LNG activity in the industry through setting out new approaches, for example, taking an operatorship of the Donggi Senoro LNG project in Indonesia and leveraging equity volumes from Australia,” he said.
Southeast Asia, Australia assets
Since acting as an LNG import agent for the Japanese in 1969, MC has been involved in a multitude of projects and operations, including the production, transportation and trading of LNG in areas such as Singapore, Brunei, Malaysia, Australia, Oman, Indonesia, and Russia.
Brunei is the group’s first gas venture having acquired 25% interest in the Brunei LNG project in 1970, partnering the Bruneian government and Shell, who hold 50% and 25% respectively. Located at Lumut in the Belait District, the plant pumps about 6.7mn mt/yr of LNG for export. MC’s share, 1.8mn mt/yr, is sold to long term Japanese customers – Jera, Tokyo Gas, Osaka Gas, and Korea Gas – while the rest is sold to Shell, Petronas LNG, and the spot market. In 2015 alone, about 6,500 cargoes were delivered to Japan.
MC is also a minority shareholder in the Malaysia LNG project in Sarawak, consisting of three LNG plants: Malaysia LNG Satu, Malaysia LNG Dua, and Malaysia LNG Tiga, in the Petronas LNG plant in Bintulu. The combined LNG production capacity of the three plants totals 30mn mt/yr and much of it is sold to utilities in Japan, China, South Korea, and Taiwan. Shareholders of Malaysia LNG Satu include operator Petronas (90%), the Sarawak state government (5%), and MC (5%). Similarly, the three groups also partner in Malaysia LNG Dua, holding 80%, 10% and 10% stakes respectively.
MC shares a 5% interest in Malaysia LNG Tiga with Japex, while Petronas has the majority 60%, the Sarawak government 10%, Shell 15%, and JX Nippon Oil & Energy 10%. The firm is entitled to 1.69mn mt/yr of LNG collectively from all three plants that are being sold to Tohuku Electric, Tokyo Gas, Osaka Gas, Shanghai LNG, JX Nippon, and Kansai Electric, among others.
Australia, a country that has seen the birth of several mega LNG projects, is another interest area for MC. In 1985, it became one of the six partnering companies to invest in the $34bn NorthWest Shelf (NWS) project in Perth, Western Australia. It includes the Karratha Gas Plant, where LNG, domestic gas, condensate and liquid petroleum gas are produced and exported to Japan and the broader Asia-Pacific region.
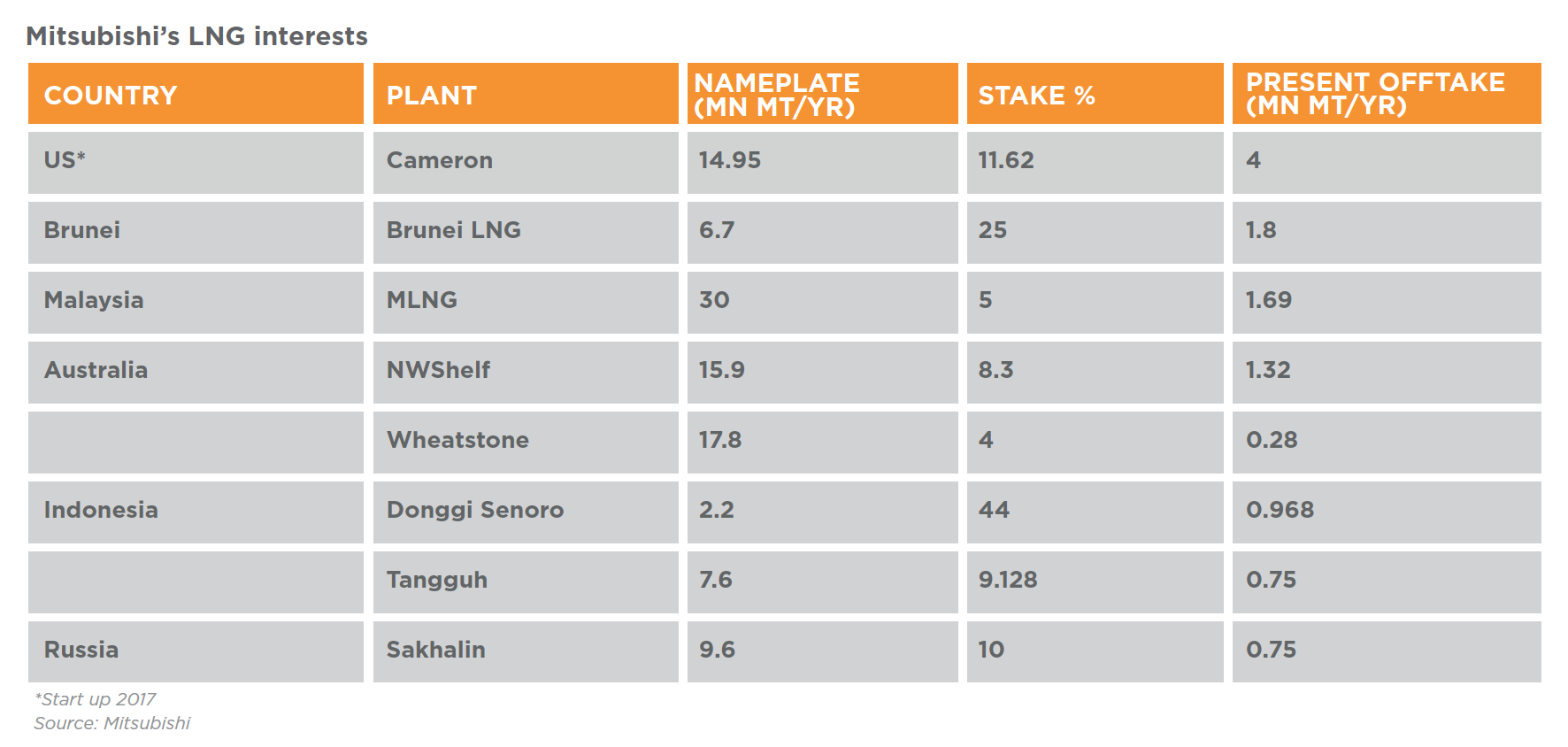
Operated by Woodside (16.67%), the other equal participants of NWS are BHP Billiton, BP, Chevron, Shell and Japan Australia LNG, a 50:50 joint venture business between MC and Mitsui & Co. MC’s share of the 1.36mn mt/yr from NWS is sold to Guandong Dapeng LNG, Chugoku Electric, Jera, Toho Gas, Kansai Electric, Kyushu Gas, and Tokyo Gas.
Similarly, Japan Australia LNG joins Woodside in the stalled Browse LNG development in Broome, Western Australia. Last year, forced by the collapse in oil prices, the joint venture together with Shell, BP and PetroChina, decided not to progress further with the floating LNG concept. The team is now in the midst of assessing a range of development ideas, hoping to reach a decision this year, and possibly start front-end engineering and design in 2019.
Scheduled to start production in September, MC became an investor in the $34bn Wheatstone LNG development in 2012. It is a joint venture between the US operator Chevron (64.14%), Kuwait Foreign Petroleum Exploration Company (13.4%), Woodside (13%), Kyushu Electric Power Company (1.46%), and PE Wheatstone (8%), owned by MC and Jera.
Situated in Onslow in Western Australia’s Pilbara region, the foundation project includes two LNG trains with a combined capacity of 8.9mn mt/yr. MC’s share of the pie totals 0.28mn mt/yr and it has already locked in sales contracts with Kyushu Electric, and Tohoku Electric.
Up in Indonesia, MC is a major shareholder in the PT Donggi Senoro LNG plant in Central Sulawesi. With a production capacity of 2.2mn mt/yr, the plant delivers around 36 cargoes of LNG annually to long-term Asian buyers Chubu Electric, Kyushu Electric, and Korea Gas. Sulawesi LNG Development a 75:25 joint venture company between MC and Korea Gas holds 59.9% interest in the project, along with PT Pertamina Hulu Energi (29%), and PT Medco LNG Indonesia (11.1%).
Similarly, MC has an investment in the Tangguh LNG facility in the Papua Barat Province of Indonesia. It consists of offshore gas production facilities supplying two 3.8mn mt/yr liquefaction trains that have been in operation since 2009. Tangguh partners are the UK operator BP (40.22%), Cnooc (13.9%), JX Nippon (12.23%), and Indonesian KG Berau Petroleum and KG Wiriagar Petroleum (10.00% together), Indonesia Natural Gas Resources Muturi (7.35%), and MI Berau (16.30%), which is a 56:44 company of MC and Inpex.
Last year, Tangguh achieved its 700th cargo, and welcomed the final investment decision to add a third LNG process train, bringing total plant capacity to 11.4mn mt/yr. LNG from the new train will be sold to Indonesian state electricity company PLN Persero with the rest going to Kansai Electric under a term contract. MC sells its 0.75mn mt/yr offtake to Fujian LNG, Sempra Energy, and Tohoku Electric, among others.
MC has been investing in Russian reserves since 1994 after gaining 10% equity interest in what became Gazprom’s Sakhalin II LNG project, alongside Shell (27.5%), and Mitsui (12.5%). The company’s share of LNG from Sakhalin totals 0.75mn mt/yr which is exported to Jera, Tokyo Gas, Hiroshima Gas, Korea Gas, and Osaka Gas. The partners, led by Shell, and Gazprom are still in talks about building a third train.
New market ventures
Going forward, MC and DGI aim to play a role in developing the emerging LNG market, Tsugaru said, adding that “helping emerging buyers who plan to import LNG, would eventually help the LNG industry as a whole as it promotes industry growth and improves supply-demand fundamentals.
“This would eventually help our existing customers as well. DGI is functioning as the marketing arm for MC and is up against these challenges to open up new markets especially east of Suez. One example of DGI’s efforts is a planned LNG import project in Pakistan, now under development together with partners Qatar Petroleum, ExxonMobil, Total, Hoegh LNG, and Global Energy,” he said.
The project includes a floating storage and regasification unit (FSRU), a jetty, and a pipeline to shore to provide natural gas supply to Pakistan. The FSRU, currently advancing through technical and commercial milestones, will have a minimum regasification capacity of 750mn ft³/d by 2018.
Furthermore, as international regulations on emissions for ships tighten, LNG is expected to become an important alternative fuel for the maritime industry. To tap into this emerging market, in September 2016, MC, Engie and NYK launched a commercial brand, Gas4Sea, specifically designed for LNG bunkering. In June, the bunkering vessel Engie Zeebrugge performed in the port of Zeebrugge, Belgium, its first deliveries of LNG as a marine fuel for two United European Car Carriers vessels.
This comes after MC reached an agreement with Tenaska in April 2016, to develop a natural gas-fired power generation project in Pennsylvania. Working through its Diamond Generating Corporation subsidiary, MC will hold a 50% equity share in the project while Tenaska holds the remaining 50%. Scheduled to start commercial operations in 2019, the project involves the construction and operation of a natural gas-fired combined-cycle power plant with a capacity of 925 MW.



